Car loan calculator empowers you to navigate the complexities of car financing. It’s a crucial tool for understanding the costs and terms of various loan options, enabling informed decisions. From fixed-rate to variable-rate loans, this guide walks you through the process of comparing offers and choosing the best fit for your needs.
This comprehensive resource details the essential elements of a car loan calculator, from input parameters to calculation methodologies. We delve into different loan types, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. Ultimately, this will empower you to make a well-informed choice when it comes to securing a car loan.
Introduction to Car Loan Calculators
Car loan calculators are invaluable tools for anyone considering purchasing a vehicle. They streamline the complex process of determining affordable loan terms and provide a clear picture of the financial commitment involved. These tools are widely accessible online and offer a user-friendly interface for estimating monthly payments, total interest paid, and the overall cost of the loan.A car loan calculator essentially acts as a financial simulation, allowing users to experiment with different loan parameters to assess their affordability and choose the best possible loan option.
This helps potential car buyers make informed decisions, compare offers, and ultimately avoid costly financial mistakes.
Purpose and Function of a Car Loan Calculator
A car loan calculator’s primary function is to compute the monthly payments and total cost of a car loan based on user-provided input. This enables individuals to quickly evaluate various loan options and understand the financial implications before committing to a purchase. By inputting variables like loan amount, interest rate, and loan term, the calculator automatically calculates crucial details, such as the monthly payment, total interest, and the overall loan cost.
This helps in comparing different loan offers from various lenders and facilitates a more informed decision-making process.
Typical Input Fields in a Car Loan Calculator
Car loan calculators typically feature a variety of input fields. These fields allow users to customize the loan scenario and receive tailored results. Common input fields include:
- Loan Amount: This field represents the principal amount borrowed for the car purchase. It’s crucial for determining the overall cost of the loan and subsequent monthly payments.
- Interest Rate: This field reflects the annual percentage rate (APR) charged by the lender. Different lenders offer varying interest rates, and this input field allows for comparison of loan offers based on the interest rate component.
- Loan Term: This indicates the duration (typically in months or years) over which the loan is to be repaid. A longer loan term often leads to lower monthly payments but increases the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
- Down Payment: A down payment is an upfront payment made by the buyer. This field allows users to input the down payment amount, which significantly impacts the loan amount and the overall cost of the loan. A higher down payment reduces the loan amount, leading to potentially lower monthly payments and less total interest paid.
- Additional Fees: This field can accommodate any additional fees associated with the loan, such as origination fees or other charges. These fees can significantly affect the overall cost of the loan, so incorporating them is crucial for accurate estimations.
Common Features Offered by Different Car Loan Calculators
Different car loan calculators offer various features beyond the core calculation functionality. These extra features enhance the user experience and provide a more comprehensive overview of the loan.
- Payment Breakdown: Many calculators provide a detailed breakdown of each monthly payment, showing the portion allocated to principal and interest. This transparency helps users understand how their payments are distributed over time.
- Total Interest Calculation: This feature calculates the total interest paid over the life of the loan. This is vital for understanding the true cost of the loan beyond the monthly payments.
- Comparison Charts: Some calculators allow users to compare different loan options side-by-side. This facilitates the selection of the most favorable loan term, interest rate, and monthly payment.
- Loan Term Comparison: Calculators often display the monthly payments and total interest costs for different loan terms. This feature assists users in making informed choices regarding loan duration and their affordability.
Importance of Accuracy in Car Loan Calculations
Accurate car loan calculations are paramount for informed financial decision-making. Inaccurate calculations can lead to overpaying on a loan or failing to adequately assess the affordability of a particular vehicle.A precise understanding of monthly payments, total interest, and overall loan cost is crucial for budget planning and financial responsibility. Using a reliable and accurate calculator minimizes the risk of financial surprises and enables the selection of a suitable loan option.
Determining Monthly Payments with a Car Loan Calculator
To determine monthly payments, input the required information into the calculator. This includes the loan amount, interest rate, loan term, and down payment. The calculator will then calculate the monthly payment amount based on the inputs.
Example: If a loan amount of $25,000 is taken at an interest rate of 6% over a 60-month term, the monthly payment is approximately $480.
This example illustrates how a car loan calculator can swiftly and precisely calculate the monthly payment, empowering users to make well-informed decisions.
Different Types of Car Loans
Choosing the right car loan can significantly impact your financial well-being. Understanding the various types of loans available, their associated features, and the factors influencing their interest rates is crucial for making an informed decision. Different loan structures cater to diverse financial situations and preferences, leading to varying monthly payments and overall costs.
Fixed-Rate Loans
Fixed-rate car loans offer a consistent interest rate throughout the loan term. This predictability allows borrowers to budget effectively and understand their exact monthly payments. The interest rate is set at the time of loan origination and remains unchanged, regardless of fluctuations in market interest rates. This stability is beneficial for borrowers who prefer certainty and predictability in their financial planning.
Variable-Rate Loans
Variable-rate car loans, conversely, feature interest rates that adjust periodically, often tied to a benchmark rate like the prime rate. These adjustments can lead to fluctuations in monthly payments, making budgeting more challenging. While variable rates might initially offer lower interest rates than fixed rates, potential increases in the future should be carefully considered. Borrowers who are comfortable with fluctuating payments and anticipate potential rate decreases might find this option suitable.
Subprime Loans
Subprime car loans are designed for borrowers with less-than-ideal credit histories. These loans often carry higher interest rates compared to prime loans due to the increased risk associated with the borrower’s credit profile. Lenders often assess various factors like credit score, debt-to-income ratio, and employment history to determine eligibility and the appropriate interest rate. While these loans can make car ownership accessible to some individuals, the higher interest rates will translate to a larger total cost over the loan term.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Several key factors influence the interest rate assigned to a car loan. The borrower’s credit score is a primary determinant, as higher scores typically indicate lower risk and thus lower interest rates. The loan term also plays a role; longer terms generally lead to higher interest rates. The prevailing market interest rates, the value of the vehicle, and the lender’s lending policies are also significant factors in determining the final interest rate.
Impact of Loan Terms on Monthly Payments
The loan term directly affects the monthly payment amount. Shorter loan terms result in higher monthly payments but a lower total interest paid over the loan’s lifetime. Conversely, longer loan terms reduce monthly payments but increase the total interest paid. Borrowers should carefully consider their budget and long-term financial goals when selecting a loan term.
Pros and Cons of Each Loan Type
| Loan Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed-Rate | Predictable monthly payments, budgeting certainty | Potentially higher initial interest rates compared to variable rates |
| Variable-Rate | Potentially lower initial interest rates | Fluctuating monthly payments, increased risk of higher interest rates in the future |
| Subprime | Can make car ownership accessible to individuals with less-than-ideal credit | Significantly higher interest rates, potentially higher total cost over the loan term |
Input Parameters for Calculation
A car loan calculator relies on specific input values to determine the monthly payment and overall loan cost. Understanding these parameters is crucial for accurately assessing the financial implications of a car loan. These inputs allow users to simulate different scenarios and compare loan options.
Input Parameters Table
This table Artikels the key input parameters required for a car loan calculation, along with descriptions and examples. Accurately providing these values is essential for generating precise and reliable results.
| Parameter | Description | Realistic Example |
|---|---|---|
| Loan Amount | The total principal amount borrowed for the vehicle. | $25,000 |
| Interest Rate | The annual interest rate charged on the loan, typically expressed as a percentage. | 6.5% |
| Loan Term (in months) | The duration of the loan in months. | 60 months (5 years) |
| Down Payment | The initial payment made by the borrower before the loan. | $5,000 |
Relationship Between Parameters and Loan Outcome
The relationship between the input parameters and the final loan outcome is a direct correlation. A higher loan amount, interest rate, or loan term will typically result in a higher monthly payment. Conversely, a higher down payment will reduce the loan amount and lower the monthly payment. These factors are interconnected, meaning a change in one parameter will affect others.
Impact of Parameter Changes on Monthly Payment
Changes in the input parameters significantly affect the monthly payment. For instance, increasing the loan amount, interest rate, or loan term directly leads to a higher monthly payment. Conversely, a larger down payment reduces the loan amount and, consequently, the monthly payment. This direct relationship underscores the importance of carefully considering these factors when evaluating a car loan.
Example: A $25,000 loan at 6.5% interest for 60 months results in a monthly payment of approximately $480. Increasing the loan term to 72 months (6 years) would increase the monthly payment to roughly $430.
Calculation Methodology: Car Loan Calculator

Understanding the mathematical underpinnings of car loan calculations is crucial for making informed financial decisions. These calculations determine the monthly payments, total interest paid, and the overall cost of borrowing. This section delves into the specifics of these calculations, providing a step-by-step guide to comprehend the process.
Formulas Used in Car Loan Calculations
The core formula for calculating monthly car loan payments is based on the present value of an annuity. This formula considers the principal loan amount, the interest rate, and the loan term. A simplified version of this formula is frequently used:
M = P [ i(1 + i)^n ] / [ (1 + i)^n – 1]
Where:* M = Monthly Payment
- P = Principal Loan Amount
- i = Monthly Interest Rate (annual interest rate divided by 12)
- n = Total Number of Payments (loan term in months)
Steps Involved in Calculating Monthly Payments
Calculating monthly payments involves several crucial steps, Artikeld below:
- Determine the principal loan amount. This is the initial amount borrowed for the car.
- Establish the annual interest rate. This is the percentage rate charged by the lender for borrowing the money.
- Identify the loan term in years. This represents the duration over which the loan will be repaid.
- Convert the annual interest rate to a monthly interest rate. This is done by dividing the annual interest rate by 12.
- Calculate the total number of payments. This is achieved by multiplying the loan term in years by 12.
- Substitute the values into the formula (M = P [ i(1 + i)^n ] / [ (1 + i)^n – 1]) to determine the monthly payment.
Amortization Schedules
An amortization schedule details the breakdown of each monthly payment, showing how much goes towards principal and interest. This schedule provides a clear picture of the loan’s repayment trajectory. It’s a valuable tool for tracking progress and understanding the total cost of borrowing over the loan’s life.
Figuring out your car loan calculator options can be tricky, especially when unexpected repairs pop up. For example, if your transmission needs work, transmission repair costs can significantly impact your budget and potentially affect your loan terms. Ultimately, understanding these factors is key to selecting the best car loan calculator for your situation.
- The first step involves calculating the interest portion of the first payment. This is determined by multiplying the outstanding principal balance by the monthly interest rate.
- The principal portion of the payment is calculated by subtracting the interest portion from the total monthly payment.
- The new principal balance is then calculated by subtracting the principal portion from the previous principal balance.
- These steps are repeated for each subsequent payment, systematically reducing the principal balance and showing the diminishing interest component.
Step-by-Step Guide for Understanding the Calculation Process
This section offers a detailed guide, making the calculation process more understandable.
- Gather necessary data: Obtain the principal loan amount, annual interest rate, and loan term.
- Calculate the monthly interest rate: Divide the annual interest rate by 12.
- Determine the total number of payments: Multiply the loan term in years by 12.
- Apply the formula: Substitute the gathered data into the formula (M = P [ i(1 + i)^n ] / [ (1 + i)^n – 1]) and solve for the monthly payment (M).
- Create an amortization schedule: Use the calculated monthly payment to determine the interest and principal components for each payment, tracking the decreasing principal balance.
Loan Comparison and Analysis
Comparing car loan offers from different lenders is crucial for securing the most favorable terms. A careful analysis of various loan options can save you a significant amount of money over the life of the loan. Understanding the factors influencing interest rates and payment amounts is key to making an informed decision.
Comparing Results from Different Calculators
Different car loan calculators, even reputable ones, may produce slightly varying results due to differing methodologies and assumptions. These differences, while often minor, can accumulate over the loan term, impacting the total cost. These differences in calculated payments can be attributed to the calculation methods, the assumed interest rate models, and potential variations in fees or charges.
Examples of Varying Results
Consider a hypothetical scenario where you’re looking at a $25,000 car loan with a 60-month term. Calculator A might estimate a monthly payment of $500, while Calculator B might calculate a payment of $505. This seemingly small difference compounds over time, resulting in a total interest paid that varies. The differences might stem from slight variations in the interest rate calculation model or in how fees and charges are factored into the payment calculation.
Factors Influencing Payment Differences
Several factors contribute to the variations in calculated payments across different calculators. These include the assumed interest rate model (e.g., simple interest, compound interest), the compounding frequency (daily, monthly, annually), and the inclusion of additional fees or charges. Even slight differences in these elements can significantly impact the final payment amount.
Impact of Credit Score on Interest Rates
A borrower’s credit score significantly influences the interest rate offered by lenders. A higher credit score typically translates to a lower interest rate, leading to lower monthly payments and overall cost of borrowing. For example, a borrower with a credit score of 750 might receive an interest rate of 4.5%, while a borrower with a credit score of 650 might receive an interest rate of 6%.
This difference in rates directly impacts the total amount paid over the loan term.
Loan Offer Comparison Table
| Lender | Interest Rate (%) | Monthly Payment ($) | Total Interest ($) | Loan Term (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 4.8 | 510 | 5,000 | 60 |
| Credit Union B | 4.5 | 500 | 4,500 | 60 |
| Online Lender C | 5.0 | 515 | 5,200 | 60 |
This table demonstrates a comparison of loan offers from three different lenders. Notice how the slight differences in interest rates lead to varying monthly payments and total interest amounts. The loan term is kept consistent for a fair comparison. By analyzing such tables, you can make an informed decision regarding which loan offer best suits your needs.
Factors Influencing Car Loan Costs
Understanding the factors influencing car loan costs is crucial for borrowers to make informed decisions. This section delves into the key elements impacting the interest rate, loan terms, and overall cost of a car loan. From creditworthiness to market conditions, these factors collectively shape the financial burden of acquiring a vehicle.
Credit Score’s Impact on Interest Rates
Credit scores are a critical determinant of interest rates for car loans. Lenders assess creditworthiness to gauge the borrower’s ability to repay the loan. A higher credit score indicates a lower risk to the lender, leading to a lower interest rate. Conversely, a lower credit score increases the perceived risk, resulting in a higher interest rate. This difference in rates can significantly impact the total cost of the loan over the loan term.
For example, a borrower with a 750 credit score might secure a 4% interest rate, whereas a borrower with a 650 credit score could face a 6% interest rate, leading to thousands of dollars in additional interest paid over the life of the loan.
Down Payment’s Influence on Loan Terms
A larger down payment reduces the loan amount. This translates to a lower principal balance for the loan, potentially leading to lower monthly payments and a shorter loan term. Lenders view a substantial down payment as a positive signal of the borrower’s financial responsibility, which often translates to more favorable loan terms. A 20% down payment, for instance, is often a benchmark for securing the most favorable loan terms, reducing the loan amount and monthly payments.
Loan Term’s Impact on Monthly Payments and Total Interest
The loan term, or the duration of the loan, directly affects both monthly payments and the total interest paid. A shorter loan term results in higher monthly payments but typically lower total interest. Conversely, a longer loan term lowers monthly payments but increases the total interest accumulated. This is a classic trade-off: borrowers prioritize lower monthly payments, but it will increase the overall cost of the loan over time.
For instance, a 5-year loan will have higher monthly payments than a 7-year loan, but the total interest paid will be significantly less.
Market Interest Rates’ Effect on Loan Costs
Current market interest rates play a significant role in determining the cost of a car loan. When market interest rates are high, lenders charge higher interest rates on car loans. Borrowers will be faced with higher monthly payments and increased total interest costs. Conversely, during periods of low market interest rates, car loan interest rates tend to be lower.
For instance, a significant increase in the prime interest rate might cause lenders to increase their interest rates on car loans, increasing the overall cost for the borrower.
Table of Factors Influencing Car Loan Costs, Car loan calculator
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Credit Score | Higher credit scores typically result in lower interest rates, reducing the overall cost of the loan. |
| Down Payment | A larger down payment decreases the loan amount, potentially lowering monthly payments and the total interest paid. |
| Loan Term | Shorter loan terms lead to higher monthly payments but lower total interest, while longer terms result in lower monthly payments but higher total interest. |
| Market Interest Rates | Higher market interest rates generally increase car loan interest rates, increasing the total cost of the loan. |
Tips for Choosing a Car Loan
Securing the right car loan hinges on careful consideration and strategic planning. Understanding the nuances of loan terms, fees, and negotiation tactics empowers you to make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals. This section provides practical advice to help you navigate the process successfully.
Negotiating Loan Terms
Effective negotiation is crucial for securing favorable loan terms. A proactive approach, combined with a thorough understanding of your financial situation and the market rates, can yield substantial savings.
To negotiate effectively, research current market interest rates and compare them to the rates offered by different lenders. Prepare a comprehensive understanding of your creditworthiness and the specifics of the car you intend to purchase. This allows for informed discussions and positions you to confidently advocate for your best interests. A pre-approval for a loan from a lender can also provide you with a stronger bargaining position.
Comparing Loan Offers
Comparing loan offers from multiple lenders is essential for securing the most advantageous terms. This involves carefully analyzing interest rates, loan amounts, and associated fees to make a well-informed choice.
A crucial aspect of comparing loan offers is examining the total cost of borrowing. This includes not only the interest rate but also any upfront fees or charges. Employ a loan comparison tool or spreadsheet to systematically organize and compare the offers. Consider factors like the loan term and any additional fees to determine the true cost of the loan.
| Lender | Interest Rate | Loan Term (years) | Upfront Fees | Total Estimated Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 6.5% | 5 | $300 | $10,000 |
| Credit Union B | 6.2% | 5 | $200 | $9,800 |
| Online Lender C | 6.8% | 4 | $150 | $9,700 |
The table above demonstrates a comparison of loan offers. Notice that while Bank A has a slightly lower interest rate, Credit Union B offers a lower total estimated cost due to lower fees, despite the marginally higher interest rate. Loan term length is also a significant factor; a shorter term typically leads to lower overall costs.
Considering Loan Fees and Charges
Loan fees and charges can significantly impact the overall cost of your car loan. Understanding these fees and charges allows you to make an informed decision.
Carefully scrutinize all loan documents for details on origination fees, prepayment penalties, and any other associated charges. These fees can often be overlooked, but they can significantly inflate the overall cost of the loan. Seek clarification on any fees or charges that are unclear. It is essential to consider all potential costs before committing to a loan agreement.
“Thorough understanding of all fees and charges is critical for accurately assessing the true cost of the loan.”
Steps in Choosing a Car Loan
A systematic approach to choosing a car loan can significantly improve your chances of securing the best possible terms. Following these steps will help you navigate the process effectively.
- Research and Compare: Thoroughly research different lenders and compare interest rates, loan terms, and associated fees.
- Evaluate Credit Score: Understand your current credit score and the impact it has on loan approval and interest rates. If necessary, take steps to improve your credit score.
- Determine Budget: Determine a realistic budget for your car loan payments and make sure it aligns with your financial situation.
- Negotiate Terms: Negotiate with lenders to secure the most favorable interest rate and loan terms.
- Review Loan Documents: Carefully review all loan documents and understand all fees and charges before signing any agreement.
Future Trends and Innovations
The car loan market is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. This dynamic environment presents exciting opportunities for innovation in both calculator design and loan offerings themselves. Understanding these trends allows potential borrowers to make informed decisions and lenders to adapt to changing circumstances.
Potential Advancements in Car Loan Calculators
Car loan calculators are poised for significant advancements, moving beyond basic calculations to incorporate more sophisticated features. This evolution will likely include enhanced user interfaces, offering intuitive navigation and a more personalized experience. Furthermore, calculators could integrate real-time data feeds for current market rates and loan terms, dynamically updating calculations to reflect the most current information. This would provide borrowers with a more responsive and accurate assessment of their options.
Integration of New Technologies
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) hold significant promise for transforming car loan calculators and the overall lending process. AI-powered calculators can analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and predict potential risks, leading to more precise assessments of loan applications. ML algorithms could personalize loan recommendations based on individual credit scores, financial history, and other factors, tailoring the offered terms to the specific borrower’s profile.
Figuring out a car loan calculator can be tricky, but it’s crucial for budgeting. Knowing your monthly payments is essential, but don’t forget about the ongoing maintenance, like brake repair , which can impact your finances. Ultimately, a comprehensive approach to car ownership, including the loan calculator, is key for a smooth experience.
Future Trends in the Car Loan Industry
Several key trends are shaping the future of car loans. The increasing prevalence of online lending platforms suggests a continued shift towards digital transactions and streamlined applications. Furthermore, the rise of subscription-based car ownership models might lead to innovative loan structures that better accommodate these emerging financing options.
Potential Areas for Innovation in Car Loan Offerings
The car loan market can expect novel loan products tailored to specific consumer segments. For example, specialized loans for environmentally friendly vehicles or electric vehicles (EVs) could emerge, reflecting the growing demand for sustainable transportation. Innovative financing solutions for specific demographics, such as first-time car buyers or individuals with limited credit history, could also gain traction. These tailored approaches would provide more accessible options for a wider range of borrowers.
Potential Changes in the Car Loan Market
Current trends suggest a market moving toward greater transparency and personalized financial solutions. This shift will likely be reflected in more detailed and accessible loan terms, with greater emphasis on user-friendly calculators and financial education tools. Further, competitive pricing will become even more critical, potentially leading to the development of novel pricing strategies that factor in various consumer data points, including environmental impact and individual financial profiles.
This competitive environment will demand a sophisticated approach to risk assessment and loan structuring.
Illustrative Examples and Scenarios
Understanding car loan calculations is crucial for informed decision-making. This section provides practical examples and scenarios to illustrate how different factors impact loan costs and terms. Realistic scenarios demonstrate the potential financial implications of various loan choices.
Impact of Loan Terms on Total Interest Paid
Loan terms, specifically the length of the loan, significantly affect the total interest paid. A shorter loan term typically results in lower overall interest but higher monthly payments. Conversely, a longer loan term leads to higher total interest over the life of the loan but lower monthly payments. The following table illustrates this impact.
| Loan Term (Years) | Monthly Payment (USD) | Total Interest Paid (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 600 | 1,500 |
| 5 | 400 | 2,500 |
| 7 | 300 | 3,500 |
| 10 | 250 | 5,000 |
This table showcases a simplified example. Actual figures will vary depending on the principal loan amount, interest rate, and other factors. Consider the different monthly burdens associated with different terms.
Scenarios of Different Loan Types
Different types of car loans, such as fixed-rate and variable-rate loans, have distinct implications for borrowers. A fixed-rate loan offers a stable monthly payment throughout the loan term, predictable interest payments, and the potential to lock in a favorable rate. A variable-rate loan, on the other hand, has fluctuating monthly payments and interest rates, which can either benefit or disadvantage the borrower depending on market conditions.
Loan Application and Outcomes
The process of applying for a car loan can vary. Factors like credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio significantly influence loan approval and interest rates. A strong credit history often translates to better interest rates and loan approval chances. Conversely, a lower credit score may lead to higher interest rates or loan denial.
Loan Amortization Schedules
Loan amortization schedules visually display the breakdown of loan payments over time. The schedule shows how much of each payment goes toward principal and interest. A schedule clearly illustrates how the principal portion of the payment increases over time as the loan progresses, while the interest portion decreases. An example of a 3-year loan amortization schedule would show the payment amounts for each month, and the principal and interest components of each payment.
Realistic Examples
Consider a borrower purchasing a $25,000 car. A 5-year loan at an interest rate of 6% might result in monthly payments of approximately $470 and a total interest paid of $2,500. This example shows how seemingly small differences in interest rates or loan terms can significantly impact the total cost of the loan. Another example, a 7-year loan at 5% interest, might have a monthly payment of $350 and a total interest of $3,500.
These illustrative examples provide a realistic context for evaluating loan options.
Final Review
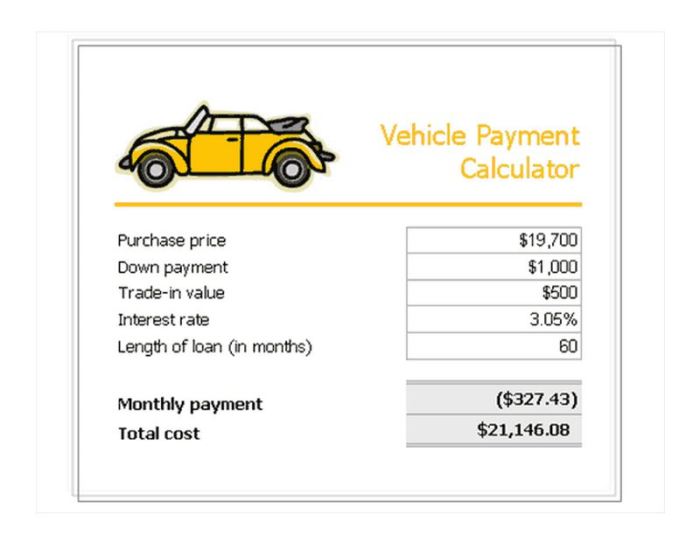
In conclusion, the car loan calculator proves an indispensable tool in the automotive financing journey. By understanding the intricacies of loan calculations, various loan types, and influencing factors, you can confidently compare offers and secure the most favorable terms. This resource equips you with the knowledge to make smart financial decisions and navigate the complexities of car financing with ease.
FAQ Insights
What are the common input fields in a car loan calculator?
Typical input fields include loan amount, interest rate, loan term, and down payment. These parameters directly impact the monthly payment and total interest paid.
How do different loan types (e.g., fixed-rate, variable-rate) impact the interest rate?
Fixed-rate loans offer a stable interest rate throughout the loan term, while variable-rate loans fluctuate based on market conditions. Factors like credit score and the lender’s risk assessment influence the interest rate for each type.
What is the impact of a higher credit score on car loan interest rates?
A higher credit score generally translates to lower interest rates, as it signifies a lower risk to the lender. This can significantly reduce the overall cost of the loan.
How can I compare loan offers from different lenders?
Comparing loan offers involves analyzing interest rates, loan terms, and associated fees. Use a car loan calculator to determine the monthly payment and total cost for each offer, allowing a direct comparison.






