Brake repair sets the stage for understanding vehicle safety and maintenance. This guide delves into various aspects of brake systems, from the different types of brakes to advanced technologies like ABS.
Understanding the intricacies of brake repair is crucial for vehicle owners. This guide provides a detailed overview, covering everything from identifying potential problems to performing repairs safely and effectively, as well as comparing DIY and professional options. The information presented aims to empower readers with knowledge and practical skills for maintaining their vehicles.
Introduction to Brake Repair
Automotive brake systems are crucial for vehicle safety and control. Proper functioning ensures safe stopping and maneuverability, preventing accidents. Understanding the different types of brakes, their components, and potential failure points is essential for effective repair and maintenance.
Types of Brakes
Brake systems utilize various technologies to slow or stop a vehicle. The two primary types are disc brakes and drum brakes. Disc brakes, employing a rotating disc and caliper with friction pads, are common in modern vehicles due to their efficiency and responsiveness. Drum brakes, which use a rotating drum and internal shoes, are less common now but still used in some applications.
Fundamental Components of a Brake System
A brake system comprises several interconnected parts working in concert to slow or stop the vehicle. Key components include the brake pedal, brake master cylinder, brake lines, wheel cylinders or calipers, brake pads or shoes, and rotors or drums. The brake pedal transmits pressure to the master cylinder, which forces hydraulic fluid through the lines to the wheel cylinders or calipers.
These components then apply pressure to the brake pads or shoes, generating friction against the rotors or drums, slowing or stopping the vehicle.
Common Causes of Brake Failure
Brake failure can stem from various issues. Worn brake pads or shoes, inadequate brake fluid levels, damaged brake lines, or faulty calipers are common causes. Corrosion, excessive heat buildup, or improperly adjusted components can also contribute to brake failure. Regular inspection and maintenance are critical to preventing such issues.
Disc vs. Drum Brake Systems
| Feature | Disc Brakes | Drum Brakes |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Friction between brake pads and a rotating disc. | Friction between brake shoes and a rotating drum. |
| Efficiency | Generally more efficient due to better heat dissipation and modulation. | Generally less efficient and less responsive, especially at high speeds. |
| Maintenance | Typically easier to maintain and inspect, requiring less frequent adjustments. | Can be more prone to wear and require more frequent adjustments. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive initially. | Generally less expensive initially. |
| Rotor/Drum Wear | Rotors are prone to wear and tear from friction. | Drums can be prone to corrosion and warping. |
| Response Time | Faster response to pedal pressure. | Slower response to pedal pressure. |
The table above provides a concise comparison of disc and drum brakes, highlighting their key differences in terms of mechanism, efficiency, maintenance, cost, and response time. Understanding these differences helps in diagnosing and addressing potential brake system issues.
Identifying Brake Problems
Properly identifying brake issues is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and preventing costly repairs. Recognizing early warning signs allows for timely intervention, preventing more significant and expensive problems down the road. A thorough inspection can uncover potential issues before they escalate into major malfunctions.Identifying brake problems involves a combination of visual inspection, listening for unusual sounds, and feeling for any anomalies during operation.
Understanding the typical signs of brake distress can help drivers catch issues early.
Common Signs of Brake Issues
Understanding the telltale signs of brake problems is essential for prompt action. Various sounds, such as squealing, grinding, or pulling sensations, can indicate underlying issues. These auditory cues are often the first indication of a potential problem. Visually inspecting the brake components is equally vital for early detection.
- Squealing: A high-pitched screeching sound often indicates worn brake pads. This sound typically increases with braking and may also be accompanied by a vibration.
- Grinding: A harsh, grinding noise typically signifies severely worn brake pads or rotors. This is a serious warning and requires immediate attention.
- Pulling: A pulling sensation while braking, often accompanied by a dragging feeling, may indicate uneven wear on brake pads, warped rotors, or a sticking caliper.
- Vibration: A vibration felt through the steering wheel or pedal during braking can point to warped rotors or uneven pad wear. It can also be caused by a problem with the wheel bearings or suspension.
- Brake Pedal Feel: A spongy or soft brake pedal may indicate low brake fluid or a leak in the hydraulic system. A very hard pedal may indicate a problem with the master cylinder or a brake line.
Inspecting Brake Pads and Rotors
Regular inspection of brake pads and rotors is essential for maintaining optimal braking performance. Visual inspection can identify significant wear or damage. Properly checking these components is a critical part of preventative maintenance.
- Brake Pads: Visually examine the brake pads for thickness. Adequate pad thickness is crucial for effective braking. Measure the remaining pad thickness with a caliper or feeler gauge. Minimum pad thickness specifications are available in the vehicle’s owner’s manual.
- Brake Rotors: Inspect rotors for any signs of warping, grooves, or excessive rust. Warped rotors can cause pulling or vibration. Grooves and excessive rust can indicate damage from overheating or friction. Ensure that the rotor surface is smooth and even.
Importance of Regular Brake Maintenance
Regular brake maintenance is a vital part of vehicle upkeep. It helps to avoid costly repairs and accidents by detecting problems early. Prompt attention to brake issues can save significant amounts of money and prevent potential harm.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular inspection and servicing of brake components help to avoid costly repairs by detecting problems early.
- Safety: Well-maintained brakes are essential for safe vehicle operation. Early detection of problems ensures reliable braking during critical moments.
- Vehicle Longevity: Prompt attention to brake issues extends the life of the vehicle’s braking system and related components.
Identifying Brake Fluid Leaks
Early detection of brake fluid leaks is essential for preventing brake system failure. A leak can quickly lead to reduced braking power, increasing the risk of accidents. Understanding common leak sources can aid in timely repair.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly check for wet spots or stains around brake lines, calipers, and the master cylinder. Pay close attention to areas where brake components connect.
- Fluid Levels: Periodically check the brake fluid reservoir level. Low fluid levels are a strong indication of a leak. Ensure that the reservoir fluid is at the correct level, as specified in the vehicle’s owner’s manual.
- Odor: Brake fluid has a distinct odor. If you detect a strong odor near the braking system, it might indicate a leak. If a pungent smell is noticed, it suggests a leak.
Common Brake Noises and Possible Causes
This table Artikels common brake noises and their potential causes. This information can aid in pinpointing the source of the problem.
| Brake Noise | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Squealing | Worn brake pads, uneven pad wear, or brake caliper issues. |
| Grinding | Severely worn brake pads, damaged rotors, or debris between pads and rotors. |
| Pulling | Uneven pad wear, warped rotors, or sticking calipers. |
| Vibration | Warped rotors, uneven pad wear, or issues with wheel bearings. |
Diagnosis and Troubleshooting: Brake Repair
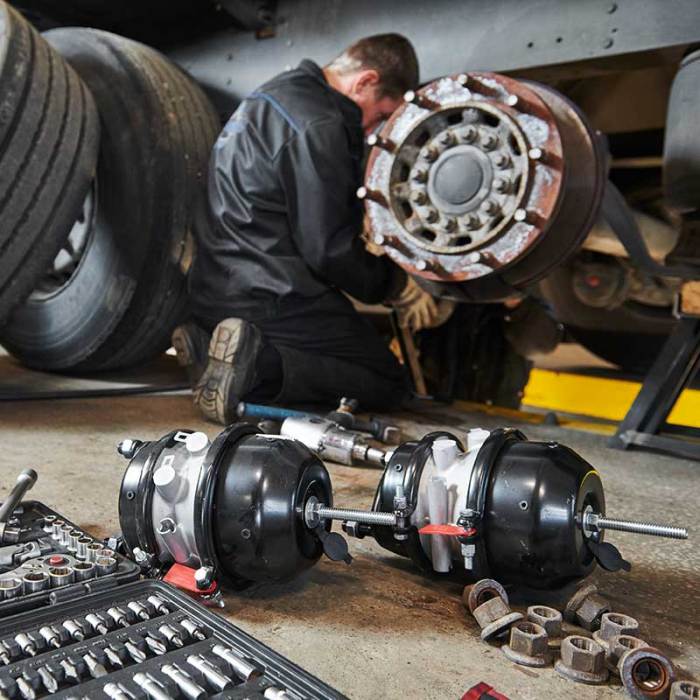

Accurately diagnosing brake problems is crucial for safe and effective repair. A systematic approach, involving careful inspection and testing, is essential to pinpoint the root cause of any malfunction. This section details the steps for diagnosing brake issues, from pressure testing to component inspections.A thorough understanding of brake system operation allows for a more precise diagnosis. The intricate network of hydraulics, mechanical linkages, and sensors must be considered when evaluating a brake problem.
This systematic approach ensures that the correct parts are addressed, preventing unnecessary replacements and ensuring a reliable repair.
Brake Pressure Gauge Usage
Proper use of a brake pressure gauge is essential for determining the health of the hydraulic system. The gauge measures the pressure within the brake lines, indicating potential leaks or malfunctions. A pressure reading below the expected range suggests a problem that needs immediate attention.The process involves connecting the gauge to the appropriate port on the brake system.
The gauge should be calibrated before use. Then, the brake pedal is depressed and the gauge reading is observed. The reading should align with the manufacturer’s specifications. Deviations from the norm signal a potential issue.
Brake Line Leak Inspection, Brake repair
Inspecting brake lines for leaks is critical to identifying potential system failures. Leaks can lead to loss of hydraulic pressure, compromising the braking system’s effectiveness. Visual inspection is the first step. Using a soapy water solution, you can identify areas where air bubbles appear, indicating a leak. Carefully examine the entire line, paying close attention to bends, connections, and welds.
Brake Caliper and Component Inspection
Regular inspection of brake calipers and their components is crucial for maintaining optimal braking performance. Brake calipers house the pistons that apply pressure to the brake pads, ensuring efficient stopping. Inspect the calipers for any signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or misalignment. Check the condition of the brake pads for wear and tear, ensuring they are within the manufacturer’s recommended thickness.
Inspect the brake hoses for any signs of deterioration or leaks. Examine the piston seals for proper function and potential leaks.
Brake Rotor Inspection Procedure
Inspecting brake rotors for damage is a vital part of any brake system assessment. Damage to the rotors can compromise braking efficiency and safety. The following table Artikels a step-by-step procedure for checking brake rotors:
| Step | Action | Observation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Visually inspect the rotor surface for any signs of warping, grooves, or scoring. | Warped rotors result in uneven braking. Grooves and scoring indicate wear and tear. |
| 2 | Check for any signs of pitting or discoloration. | Pitting can lead to uneven braking. Discoloration may indicate overheating. |
| 3 | Measure the rotor thickness using a caliper. | Rotor thickness should be within the manufacturer’s specifications. |
| 4 | Feel the rotor surface for any irregularities or roughness. | Uneven surfaces may indicate damage. |
| 5 | Examine the rotor for any cracks or fractures. | Cracks or fractures compromise the rotor’s structural integrity. |
A thorough inspection of the rotors will help determine if they are suitable for continued use. Following this process will prevent potential brake failure.
Repair Procedures
Brake repair procedures demand precision and adherence to safety protocols. Improperly performed repairs can lead to compromised braking performance, potentially causing accidents. Thoroughness and attention to detail are crucial throughout the entire process.
Replacing Brake Pads
Proper brake pad replacement is essential for maintaining safe stopping power. Worn brake pads can reduce stopping distance and lead to brake squealing or grinding noises. Following the correct procedure ensures optimal performance and extends the lifespan of the brake system.
- Locate the brake pads and determine the type (e.g., semi-metallic, organic, ceramic). Note the position and orientation of the pads within the caliper.
- Using appropriate tools, carefully remove the old brake pads. This often involves using a pry bar or a special tool to dislodge the pads from the caliper.
- Inspect the caliper and rotor for damage. Any damage should be repaired or replaced before installing new pads.
- Install the new brake pads according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure the pads are properly seated and aligned.
- Carefully reassemble the brake components, ensuring all bolts and fasteners are tightened to the specified torque.
- Perform a brake system check and test the brakes for functionality.
Replacing Brake Rotors
Brake rotors are essential for friction with the brake pads, enabling the conversion of kinetic energy into heat during braking. Damaged or warped rotors can lead to uneven braking, vibrations, and reduced stopping power. Proper rotor replacement is crucial for a smooth, responsive brake system.
- Using a torque wrench, loosen and remove the mounting bolts for the rotor. Proper torque is essential to prevent damage to the rotor or the mounting hardware.
- Inspect the rotor for any damage, such as cracks, warping, or excessive wear. Warped rotors are often indicative of overheating or poor brake maintenance.
- If the rotor is damaged, replace it with a new one. Using a suitable tool, carefully clean the rotor mounting surface to remove any debris or rust.
- Ensure the new rotor fits correctly within the mounting bracket and tighten the mounting bolts to the specified torque using a torque wrench.
- Check for any signs of rubbing or vibration during the braking process. This step is critical to ensure smooth and safe braking.
Bleeding Brake Lines
Brake fluid is a crucial component of the hydraulic braking system. Air bubbles in the lines can impair braking effectiveness. Bleeding the brake lines removes air and ensures a smooth braking response.
- Locate the brake bleeder valve on the brake caliper. Proper identification of the bleeder valve is essential to ensure effective bleeding.
- Using a brake bleeder tool or a similar device, carefully open the bleeder valve. A brake bleeder tool facilitates a controlled release of air.
- Carefully add brake fluid to the reservoir while monitoring the fluid level. Maintaining the correct fluid level is essential for the system’s functionality.
- Close the bleeder valve and repeat the process until no more air bubbles are present in the system.
- Test the brakes for smooth and effective stopping power.
Replacing Brake Calipers
Brake calipers are crucial components of the braking system, applying pressure to the brake pads. Faulty calipers can lead to reduced stopping power, requiring replacement. Accurate replacement procedures are necessary for a functioning braking system.
- Disconnect the brake lines and hoses connected to the caliper. Ensure all connections are properly disconnected to avoid any leaks or damage to the lines.
- Remove the mounting bolts securing the caliper to the brake assembly. Precise removal and re-installation of the bolts are important to maintain the correct alignment.
- Carefully inspect the caliper for damage, such as cracks or leaks. Damage to the caliper may affect the braking system’s effectiveness.
- Install the new caliper according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensuring proper alignment and installation is essential to maintain braking functionality.
- Reconnect the brake lines and hoses, and bleed the brake system.
Tools Needed for Brake Repairs
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Torque Wrench | Essential for tightening bolts to the correct specifications. |
| Brake Bleeder Tool | Used for removing air from the brake lines. |
| Pliers | Used for various tasks like gripping and holding parts. |
| Screwdrivers | Used for loosening and tightening screws. |
| Pry Bar | Useful for dislodging brake pads or components. |
| Socket Set | Used for removing and installing various fasteners. |
| Brake Pad Pliers | Designed for safely and efficiently removing and installing brake pads. |
Safety Precautions During Brake Repair
Brake repair, while crucial for vehicle safety, necessitates stringent adherence to safety protocols. Neglecting these precautions can lead to serious injuries or exacerbate existing problems. Understanding and implementing these safety measures is paramount to a safe and successful repair process.Proper safety precautions minimize the risks associated with working on a vehicle’s braking system. From handling potentially hazardous materials to using appropriate lifting techniques, each step plays a vital role in ensuring the safety of the technician and the surrounding environment.
Essential Safety Gear
Adequate personal protective equipment (PPE) is critical when performing brake repairs. Failure to use appropriate safety gear can result in significant harm from exposure to various hazards. This includes, but is not limited to, the potential for chemical burns, eye injuries, and physical harm from falling objects.
- Gloves: Protecting hands from abrasions, cuts, and contact with brake fluid is essential. Using nitrile or neoprene gloves is recommended to prevent skin irritation and protect against potential chemical contamination.
- Eye Protection: Safety glasses or goggles are necessary to shield the eyes from flying debris, dust, and potential splashes of brake fluid or other materials during the repair process. A face shield may be required for added protection.
- Hearing Protection: Brake repair often involves using power tools and equipment that generate high noise levels. Using earplugs or earmuffs can prevent hearing damage.
- Appropriate Clothing: Wear long sleeves and pants to minimize skin exposure to potential hazards. Avoid loose clothing that could get caught in moving parts or become entangled.
Proper Lifting Techniques
Improper lifting techniques can lead to back injuries when handling heavy brake components. Using appropriate lifting equipment and techniques is crucial for maintaining physical well-being during brake repairs.
- Utilize Lifting Equipment: Heavy brake components, such as calipers and rotors, should always be lifted using appropriate equipment such as jack stands or hoists. Never rely solely on manual lifting.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Bend your knees, not your back, when lifting. Keep the load close to your body to maintain balance and control.
- Seek Assistance: If a component is too heavy for one person to lift safely, seek assistance from a coworker.
Risks of Working with Brake Fluid
Brake fluid is a corrosive and potentially hazardous substance. Exposure to brake fluid can cause skin irritation, eye damage, and other health issues. Proper handling and disposal of brake fluid are crucial to maintaining a safe working environment.
Brake repair is a crucial part of car maintenance, ensuring safe and reliable driving. Proper maintenance, like checking brake fluid levels and inspecting brake pads, is essential for overall vehicle health. For a comprehensive guide on all aspects of car maintenance, including brake repair, check out this helpful resource: car maintenance. Ultimately, consistent brake repair is key to preventing potential issues down the line.
- Protective Measures: Always wear gloves and eye protection when handling brake fluid. Avoid skin contact and inhalation of brake fluid vapors.
- Proper Disposal: Brake fluid should never be disposed of down the drain. Follow local regulations for proper disposal of hazardous materials. Consult with local authorities for disposal instructions.
- Spill Response: In case of a spill, clean up the area immediately using appropriate absorbent materials and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Safety Measures for Working on a Vehicle
Working on a vehicle involves potential hazards, such as falls, electrical shocks, and fire. Implementing safety precautions is essential to minimize these risks.
- Vehicle Stabilization: Ensure the vehicle is securely supported on jack stands or a hoist before performing any work under it. Never rely on the vehicle’s jack alone. Use jack stands to ensure the vehicle is properly supported and stable.
- Proper Ventilation: Maintain proper ventilation in the work area to minimize exposure to fumes and vapors from brake fluid or other chemicals.
- Turn Off the Ignition: Always turn off the vehicle’s ignition and disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components.
Potential Hazards of Improperly Functioning Brakes
Improperly functioning brakes pose significant safety risks to drivers and other road users. Understanding the potential hazards is essential for performing brake repairs effectively.
| Hazard | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Sudden brake failure | Complete loss of braking ability | Potential for accidents, serious injury, or death |
| Gradual brake failure | Progressive loss of braking effectiveness | Reduced stopping distance, increased risk of collisions |
| Brake drag | One or more brakes are continuously applying pressure | Reduced braking efficiency, potential damage to components, abnormal wear |
| Brake squeal/vibration | Unwanted noise or vibration when braking | Indication of potential component failure, can worsen over time |
Maintenance and Prevention
Regular brake maintenance is crucial for vehicle safety and longevity. Proper care extends the life of your brake system components, reducing the risk of unexpected failures and costly repairs. By understanding the importance of routine inspections, fluid changes, and appropriate pad replacement, you can proactively safeguard your vehicle’s braking system.Preventive measures significantly impact the overall performance and safety of your braking system.
A well-maintained braking system contributes to improved vehicle control, reduced stopping distances, and minimized risks associated with brake failure.
Importance of Regular Brake Inspections
Regular inspections are essential to identify potential problems early on. This proactive approach allows for timely repairs before minor issues escalate into major, costly repairs. By detecting signs of wear or damage, such as uneven pad wear, warped rotors, or fluid leaks, you can prevent brake failure and ensure optimal braking performance.
Role of Brake Fluid Changes
Brake fluid absorbs moisture over time, reducing its effectiveness and potentially leading to corrosion within the brake system. Regular brake fluid changes are crucial to maintain optimal hydraulic pressure and prevent corrosion. Changing the fluid at recommended intervals (typically every 2 years or 24,000 miles) is vital to ensure the integrity of the braking system.
Recommendations for Proper Brake Pad Replacement Intervals
Brake pad replacement intervals vary depending on driving habits, vehicle type, and environmental conditions. However, a general guideline is to replace brake pads when the pad thickness reaches a critical threshold, typically around 1/8 inch or less. Excessive wear may lead to premature brake pad replacement. In addition, frequent hard braking or aggressive driving styles can significantly reduce the lifespan of your brake pads.
Effects of Driving Habits on Brake Wear
Driving habits significantly influence brake wear. Aggressive driving, frequent hard braking, and towing heavy loads increase the wear on brake components. The frequency of hard braking, towing heavy loads, and driving styles impact the lifespan of the brake system. For example, a vehicle used primarily for highway driving with light braking will experience less brake pad wear compared to a vehicle used for frequent stop-and-go city driving.
Preventive Measures to Extend Brake Component Lifespan
- Regular Inspections: Schedule routine inspections at recommended intervals to detect early signs of wear or damage.
- Proper Driving Habits: Avoid aggressive driving styles, especially hard braking and sudden stops.
- Maintain Recommended Fluid Levels: Ensure the brake fluid level is adequate to maintain proper hydraulic pressure.
- Brake Pad Replacement at Recommended Intervals: Replace brake pads when the thickness reaches a critical threshold, typically 1/8 inch or less.
- Avoid Overloading the Vehicle: Overloading can increase brake wear, leading to quicker component degradation.
- Proper Parking Techniques: Use parking brakes effectively to minimize wear on the parking brake system.
- Proper Maintenance Practices: Adhere to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules for optimal brake system performance.
- Identify and Address Problems Promptly: Early identification and resolution of brake problems can extend the lifespan of your braking system.
Common Brake Repair Mistakes
Brake repair, while seemingly straightforward, presents numerous opportunities for errors. These mistakes, often subtle, can compromise the safety and longevity of the braking system. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for performing reliable and safe repairs.
Identifying Common Mistakes
Several recurring errors can undermine the effectiveness and safety of brake repairs. These include misidentifying the source of a problem, using incorrect parts, neglecting critical safety precautions, and overlooking crucial inspection points. Improper component selection or installation can lead to significant issues. Furthermore, inadequate attention to detail during the repair process can contribute to future failures.
Consequences of Mistakes
The consequences of these mistakes can range from minor inconveniences to serious safety hazards. A misdiagnosed problem can lead to unnecessary expense and further complications. Using the wrong parts can compromise the braking system’s performance and durability, leading to premature failure. Neglecting safety precautions can result in injury to the technician or others nearby. Failing to address underlying issues during inspection can lead to repeated repairs and ultimately more significant issues down the line.
Importance of Precise Measurements
Precise measurements are critical during brake repair. Slight variations in component placement or tightening torque can significantly impact braking performance. Mismatched component dimensions can lead to uneven wear and tear, affecting braking efficiency and safety. Incorrect torque values can result in loose connections or, conversely, overly tight components that compromise functionality.
Improper Tightening and Brake Failure
Improper tightening of brake components, such as calipers, wheel cylinders, or brake lines, can lead to brake failure. Over-tightening can damage critical parts, potentially leading to leaks or fractures. Under-tightening, on the other hand, can result in loose connections, allowing components to shift and potentially compromising the brake system’s integrity. This can manifest as a sudden loss of braking power or a gradual decline in performance. An example of this is when a wheel cylinder bolt is not tightened to the manufacturer’s specification. This can lead to the cylinder leaking, reducing the hydraulic pressure required for effective braking, and potentially resulting in a complete brake failure. Conversely, excessively tight bolts can lead to stress fractures in the cylinder or the associated components, resulting in a similar catastrophic failure.
Careful adherence to the specified torque values, often found in the vehicle’s repair manual, is essential. Consult the manual for precise torque specifications to ensure proper tightening and avoid potential hazards.
Tips to Avoid Errors
Thorough preparation, meticulous inspection, and adhering to manufacturer specifications are crucial. Before commencing any repair, thoroughly examine the vehicle’s brake system for any signs of damage or wear. Always use the correct replacement parts and ensure they are compatible with the vehicle’s make and model. Use the correct tools and ensure they are in good working condition to avoid mistakes.
Follow all safety precautions, such as disconnecting the battery and using the proper lifting equipment, when working on the brake system. Use a torque wrench to apply the correct tightening torque on all components, meticulously following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Cost Considerations of Brake Repair
Understanding the costs associated with brake repair is crucial for informed decision-making. Knowing the average prices, labor rates, and potential savings through DIY or professional services allows you to budget effectively and avoid unexpected expenses. A well-maintained braking system is vital for safety, and understanding the financial implications can help prioritize these critical repairs.
Average Cost of Brake Repairs
Brake repairs can vary significantly depending on the specific issue and the vehicle. Routine maintenance, such as pad replacement, typically falls within a more affordable range. More extensive repairs, like replacing calipers or rotors, can be more expensive. Factors like the vehicle’s make and model, the severity of the damage, and the specific parts needed all influence the total cost.
Labor Costs Associated with Different Repairs
Labor costs play a significant role in the overall repair bill. Simple tasks like pad replacement often have lower labor costs compared to complex repairs involving caliper or rotor replacements. Professional mechanics charge hourly rates, which can vary based on location and experience. For example, a simple pad replacement might take 1-2 hours of labor, whereas a caliper replacement could take 4-6 hours or more.
Comparing Prices for Brake Repair Services
Shopping around for brake repair services is essential. Get quotes from multiple mechanics and compare not only the total cost but also the specific parts included in the price. Check online reviews and recommendations to assess the reputation and quality of the service provider. Transparency in pricing and detailed estimates are vital when making informed choices.
Cost Implications of Delaying Brake Repairs
Delaying brake repairs can lead to increased costs in the long run. Minor issues, if ignored, can escalate into more significant problems, requiring more extensive and expensive repairs. For instance, a slightly worn brake pad might lead to damage to rotors if not replaced promptly. This progressive deterioration can result in substantial repair costs. Ultimately, timely repairs are more cost-effective than delaying them.
DIY vs. Professional Repair Costs
Deciding whether to undertake brake repairs yourself or hire a professional depends on your skill level, tools, and the complexity of the repair. The cost implications of each option are Artikeld below.
| Repair Type | DIY Cost (Estimated) | Professional Cost (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Brake Pad Replacement | $50-$150 (parts) + $50-$100 (labor if applicable) | $150-$300 (parts and labor) |
| Rotor Replacement | $100-$250 (parts) + $100-$200 (labor if applicable) | $250-$500 (parts and labor) |
| Caliper Repair/Replacement | $150-$400 (parts) + $150-$300 (labor if applicable) | $400-$800 (parts and labor) |
Note: These are estimated costs and may vary depending on specific circumstances. Always get a detailed quote from a professional or research specific parts costs for your vehicle.
DIY vs. Professional Brake Repair
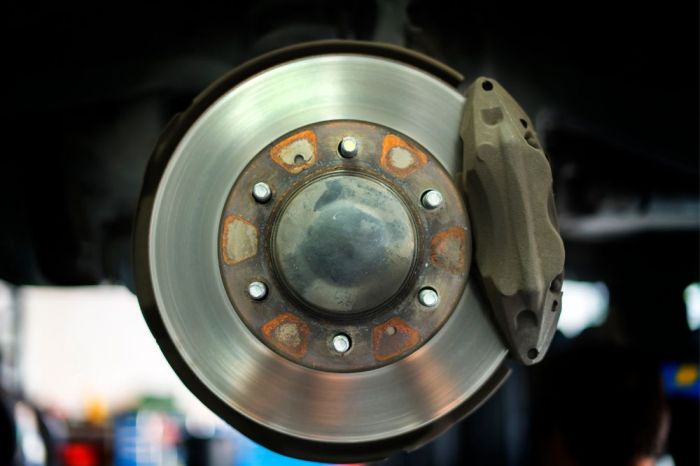

Deciding whether to tackle brake repairs yourself or enlist a professional is a crucial choice, impacting safety and vehicle longevity. A thorough understanding of the potential benefits and drawbacks of each approach is vital.
Advantages of DIY Brake Repair
DIY brake repair can offer cost savings, particularly for routine maintenance tasks like pad replacements. It also allows for a hands-on understanding of the vehicle’s mechanics. Some individuals find the process rewarding, fostering a sense of accomplishment.
Disadvantages of DIY Brake Repair
DIY brake repair carries inherent risks. Incorrect procedures can lead to compromised braking systems, posing safety hazards. Inadequate tools and specialized equipment may result in subpar repairs, and a lack of expertise can lead to further damage. Misdiagnosing a problem can worsen the issue.
Expertise Needed for Professional Brake Repair
Professional brake repair technicians possess extensive knowledge and experience. They are trained in diagnosing and troubleshooting complex brake system issues, ensuring the repair adheres to industry standards. This expertise is crucial for maintaining optimal brake performance and safety.
Risks Involved in DIY Brake Repair
The risks associated with DIY brake repair are substantial. Improperly installed parts can compromise braking efficiency, increasing the risk of accidents. Misaligned components can lead to brake failure. A poorly executed repair may necessitate further, more expensive repairs. The potential consequences of an incorrect repair extend far beyond financial costs.
Benefits of Using Professional Brake Repair Services
Professional brake repair services provide peace of mind, knowing qualified technicians are handling the job. They use advanced diagnostic tools and have access to a wider range of specialized parts. This results in more accurate diagnoses, leading to lasting repairs. Professional technicians minimize the risk of further damage.
DIY vs. Professional Brake Repair Comparison
| Feature | DIY Brake Repair | Professional Brake Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Potentially lower initial cost for simple repairs. | Higher initial cost but potentially lower long-term costs due to reliable work. |
| Safety | Increased risk of accidents due to incorrect procedures and potentially dangerous mistakes. | Reduced risk due to trained professionals and use of proper techniques. |
| Expertise | Requires significant mechanical knowledge and experience. | Expert technicians possess specialized knowledge and tools. |
| Time | Potentially time-consuming, depending on the complexity of the repair. | Typically faster due to experience and efficient procedures. |
| Warranty | Limited or no warranty on parts or repairs. | Warranty offered on parts and labor in most cases. |
Advanced Brake System Technologies
Modern brake systems have evolved significantly, incorporating sophisticated technologies to enhance safety, performance, and efficiency. These advancements address the limitations of traditional brake systems, leading to improved stopping power, reduced wear, and even energy recovery. Understanding these technologies is crucial for both maintaining vehicles and comprehending the overall advancements in automotive engineering.
Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS)
ABS systems are a vital safety feature in modern vehicles. They prevent the wheels from locking up during hard braking, maintaining steering control and reducing the stopping distance. This prevents the wheels from losing traction, which could lead to skidding, loss of control, and increased stopping distances.
Brake repair is crucial for vehicle safety. Properly maintained brakes are essential for the safe operation of all vehicles, like cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Finding a reputable mechanic for brake repair services is key to ensuring your vehicles are roadworthy and prevent accidents. Ultimately, reliable brake repair is vital for your safety and the longevity of your vehicle.
ABS systems work by monitoring wheel speed. When a wheel slows significantly, the system activates hydraulic valves to modulate brake pressure, preventing the wheel from locking up. This process is repeated rapidly to maintain control.
Regenerative Braking
Regenerative braking systems, commonly found in electric and hybrid vehicles, use the vehicle’s electric motor to recover energy during braking. Instead of dissipating energy as heat, the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is stored in the battery. This process improves fuel efficiency and reduces the reliance on traditional braking mechanisms.
Comparison of Brake Systems
| Brake System | Function | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Hydraulic Brakes | Uses hydraulic pressure to apply brake pads to rotors. | Relatively simple and cost-effective. | Energy is lost as heat, less efficient. |
| ABS | Prevents wheel lock-up during braking. | Maintains steering control, reduces stopping distance, and improves safety. | Can sometimes be less responsive during initial braking, may have slightly more complex maintenance. |
| Regenerative Braking | Recovers energy during braking using the electric motor as a generator. | Improved fuel efficiency, reduced wear on traditional brakes. | Requires an electric powertrain, may have slightly longer stopping distances at very low speeds, and may have some minor differences in the braking feel. |
Inner Workings of Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS)
The sophisticated technology within an ABS system is crucial for its effectiveness. The system constantly monitors wheel speed using sensors on each wheel. When one wheel slows significantly during braking, the ABS module rapidly modulates brake pressure. This is achieved through a complex system of hydraulic valves that adjust the pressure to each wheel, preventing wheel lock-up.
This allows the driver to maintain steering control and shorten the stopping distance.
Epilogue
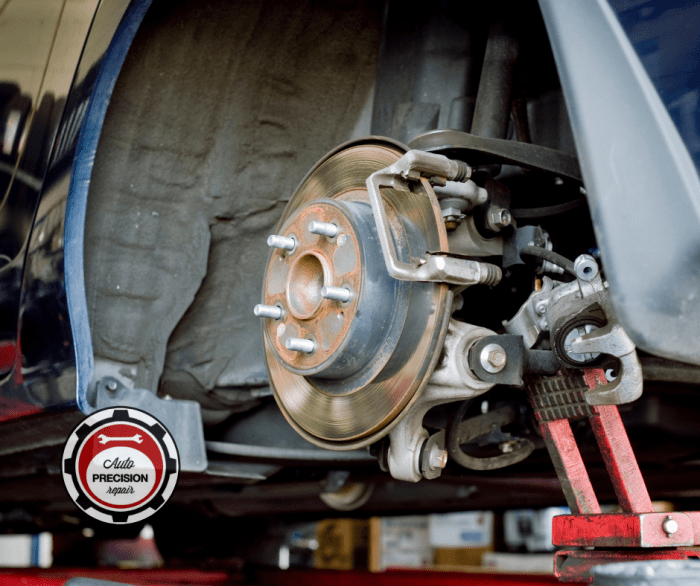
In conclusion, brake repair is a critical aspect of vehicle maintenance. By understanding the different types of brakes, common issues, and repair procedures, drivers can ensure the safety and longevity of their vehicles. This guide offers a comprehensive overview, from basic maintenance to advanced technologies. The key takeaway is that proactive maintenance is key to preventing costly repairs down the line.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the common signs of brake issues?
Common signs include squealing, grinding, pulling, and vibrations. A vehicle pulling to one side may indicate a problem with the brake system on that side.
How often should brake pads be replaced?
Brake pad replacement intervals vary depending on driving habits and conditions. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for recommended replacement schedules.
What is the difference between disc and drum brakes?
Disc brakes are generally more efficient and responsive, while drum brakes are simpler in design. Disc brakes are commonly used in newer vehicles, whereas drum brakes are found in some older vehicles.
What are the risks of working with brake fluid?
Brake fluid is corrosive and can cause skin irritation. Always wear appropriate safety gear and follow safety precautions when working with brake fluid.






